Compatibility on Corridors Overview
Compatibility on Corridors Overview
The purpose of the City of Austin's compatibility standards is to ensure that there is a transition between new, potentially taller development and less tall and dense residential development. The standards include specific requirements for building height, setbacks, scale, clustering, screening, and design. These standards may be modified by the City Council to respond to changing needs and conditions within the city.
On December 1st, 2022, the City Council adopted Ordinance No. 20221201-056, which modifies compatibility and parking standards for certain corridors to increase housing capacity and support transit investments. The ordinance reduces the distance at which compatibility standards apply, and allows greater height, and thus, more housing along the corridors in exchange for affordable housing, and reduces minimum parking requirements for residential or mixed use projects on listed corridors. On June 8th, the City Council adopted Ordinance No. 20230608-088 which amended Ordinance No. 20221201-056 to incorporate additional corridor segments which were inadvertently omitted from the previous ordinance. The corridors which were added are as follows; updated E. US 290 segment to include the section between Airport Blvd and Koening Lane as a Larger Corridor, Menchaca Rd between S. Lamar & Ben White Blvd as a Medium Corridor, Menchaca Rd between Slaughter Ln and City Limits as a Medium Corridor, and E 51st St Between Manor Rd and Ed Bluestein Blvd as a Medium Corridor.
More information about the amendment can be found in backup materials that were shared with the City Council here.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The following FAQs provide more information on the existing standards, the recently adopted changes, and where they apply.
1. What are the city-wide compatibility standards and where can I find them?
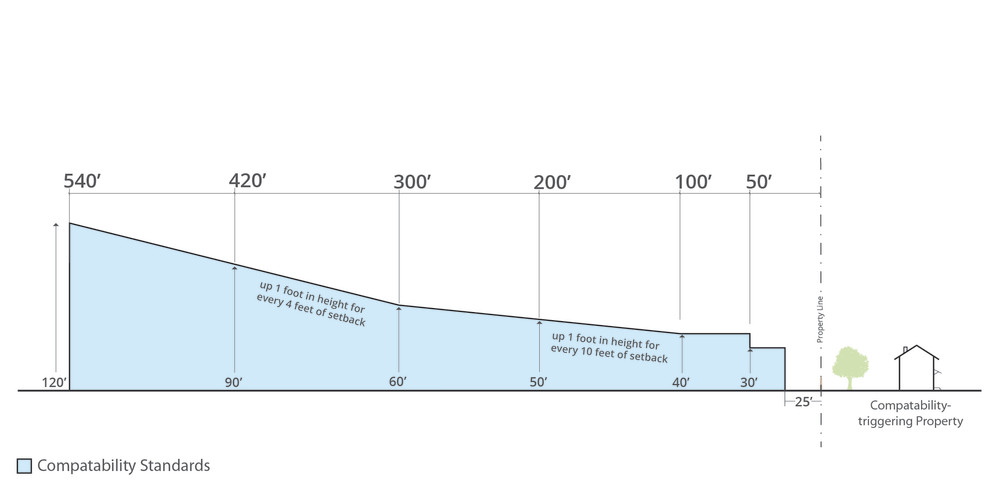
Compatibility standards can be found in Title 25, Chapter 2, Subchapter C, – Land Development, Article 10. Compatibility Standards. The City of Austin's compatibility standards generally apply to sites that are within 540 feet (or nearly two downtown blocks) of the property line of an urban family residence (SF-5) or more restrictive zoning district. Compatibility standards also apply when a site is adjacent to a lot on which a use permitted in an SF-5 or more restrictive zoning district is located.
Current compatibility standards include:
Height and Setback Limitations
Scale and Clustering Requirements
Screening Requirements
The height and setback requirements of the city-wide compatibility standards are shown in the image below. Note: Compatibility height standards are applied in addition to any restrictions that apply to a site based on its base zoning, so depending on the zoning of the site, actual allowed heights could be lower than those shown on the diagram below. For example, most commercial zoning has a 60- or 65-foot height limit.
2. What are the existing off-street parking standards and where can I find them?
The City of Austin’s existing parking requirements can be found in Title 25, Chapter 6 – Land Development, Appendix A. -Tables of Off-Street Parking and Loading 271 Requirements. For multi-family residential development, the minimum off-street parking requirements are:
- Efficiency dwelling unit: 1 space
- 1 bedroom dwelling unit: 1.5 spaces
- Dwelling unit larger than 1 bedroom: 1.5 spaces plus 0.5 space for each additional bedroom
3. What are the recently adopted changes to compatibility standards on certain corridors?
The adopted amendment generally relaxes compatibility requirements for a residential or mixed-use project on sites with frontage along a defined set of corridors: Medium, Larger, or Light Rail Corridor. For all residential or mixed-use projects on sites with frontage along a corridor:
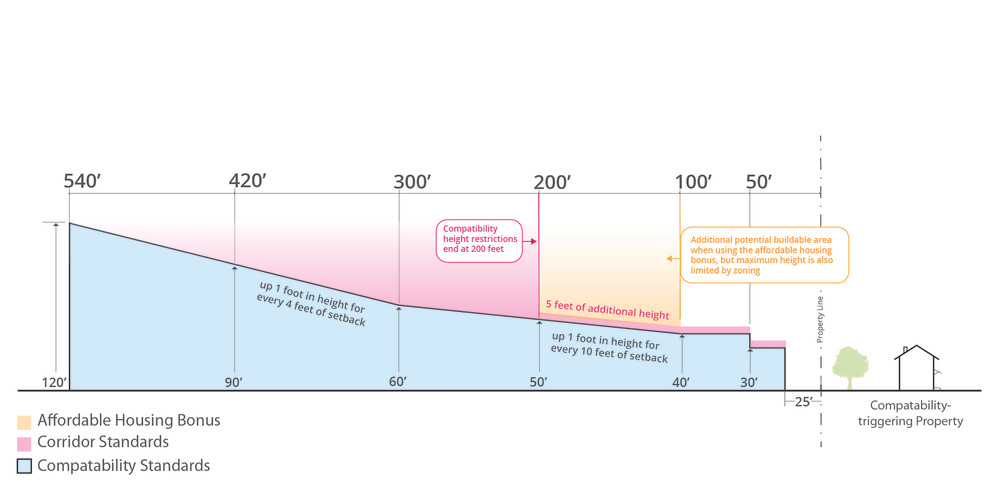
- Compatibility restrictions will end at 200’ from a triggering property on a Larger or Light Rail Corridor
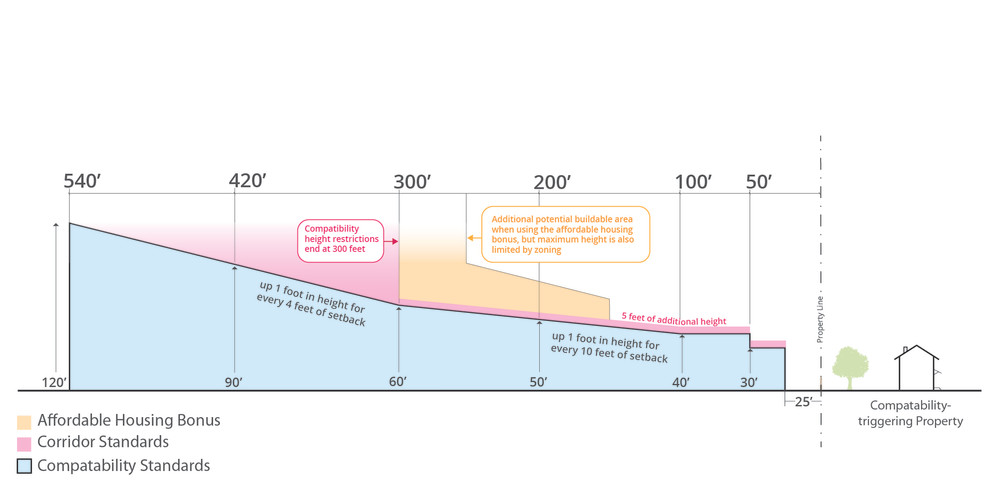
- Compatibility restrictions will end at 300’ from a triggering property on a Medium Corridor
- Compatibility restrictions will be triggered by zoning only (not by use)
- Compatibility restrictions will only apply if the triggering property is on the same side of the corridor as the site
- An additional 5’ of compatibility height will be allowed
- Projects providing affordable housing may be granted a further reduction in compatibility. For residential or mixed-use projects sites with frontage along a corridor that provides affordable housing that meets the requirements of the code:
- Compatibility restrictions will end at 100’ from a triggering property on a Light Rail Line or Large Corridor
- Compatibility restrictions will allow 65’ of height at a distance of 150’ from a triggering property and 90’ of height at 250’ from a triggering property on a Medium Corridor
- Minimum parking requirements are reduced for residential or mixed-use projects on sites with frontage along corridors:
- 25% of what would otherwise be required for a Light Rail Line or Larger Corridor
- 50% of what would otherwise be required for a Medium Corridor
The compatibility height and setback requirements that would apply to eligible projects on sites with frontage along Larger and Light Rail Line Corridors are shown in the image below compared with previous standards. Note: Compatibility height standards are applied in addition to any restrictions that apply to a site based on its base zoning, so depending on the zoning of the site, actual allowed heights could be lower than those shown on the diagram below. For example, most commercial zoning has a 60- or 65-foot height limit.
The compatibility height and setback requirements that would apply to eligible projects on sites with frontage along Medium Corridors are shown in the image below compared with previous standard. Note: Compatibility height standards are applied in addition to any restrictions that apply to a site based on its base zoning, so depending on the zoning of the site, actual allowed heights could be lower than those shown on the diagram below. For example, most commercial zoning has a 60- or 65-foot height limit.
4. Where can I see a list and a map of the specific corridors where the Corridor Overlay currently applies?
The list of Medium, Larger, and Light Rail Line Corridors are included as Exhibits A, B, and C of adopted Ordinance No. 20221201-056.
The following interactive map shows the impacted properties along Medium, Larger, and Light Rail Line Corridors overlaid on top of current zoning. You can also visit this link: bit.ly/CompatibilityCorridors to view the map in a separate window. To search for an address, go to the Settings (light) toolbar on the right, then click Map tools  and choose Search
and choose Search  . Note: this map is for informational purposes to show the general areas where the new regulations apply. This map should not be used for legal, engineering, or surveying purposes.
. Note: this map is for informational purposes to show the general areas where the new regulations apply. This map should not be used for legal, engineering, or surveying purposes.
5. How do the recently adopted changes to compatibility standards and parking regulations on certain corridors impact my property?
If you would like more information on how this regulation applies to a particular property, please contact the Development Services Department. For assistance with an appointment or to find the right work group, please call 512-978-4504, Monday – Friday, 7:45 a.m. – 4:45 p.m or visit www.austintexas.gov/page/land-development-information-services. If you need to schedule an appointment for a language other than English or Spanish, please contact 3-1-1.
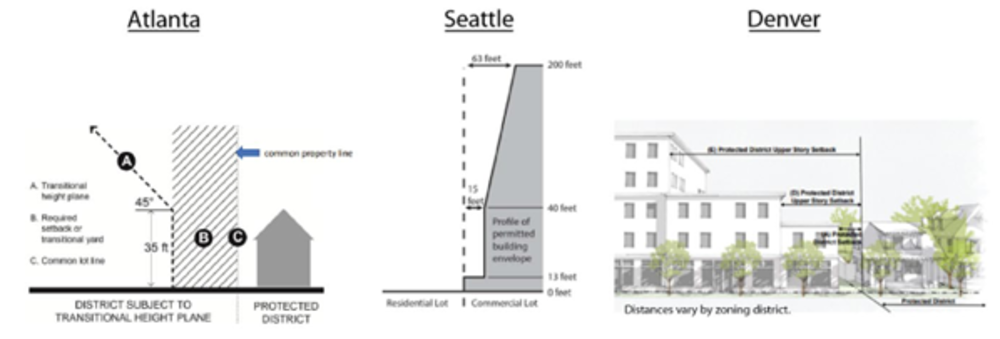
6. How do Austin’s city-wide compatibility standards compare to other cities?
Compared to similar regulations in Atlanta, Denver, and Seattle, Austin’s city-wide compatibility standards are significantly more restrictive. All three cities have regulations that require additional setbacks and height limits adjacent to low-density residential zoning districts, known as “protected districts”. In Atlanta, setbacks vary by zoning district, but under the 45-degree plane (see below) a building can reach at least 110 feet in height at 100 feet from the protected district’s property line. Seattle has the least restrictive height restrictions with buildings able to reach over 300 feet in height at 100 feet from the residential property line. In Denver, zoning districts with a height maximum of 70 feet can reach full height at 40 feet from protected district’s property line. Generally, zoning districts that allow more height are limited to 75 feet within 175 feet of the protected district; however, this height restriction does not apply to all zoning districts, building forms, and contexts.